1. Installing Python:
2. Writing Your First Python Program:


3. Basic Python Syntax:
Indentation: Python uses indentation (whitespace) to define code blocks instead of braces or parentheses. Proper indentation is crucial for code readability and functionality.
Variables: You can assign values to variables without specifying their data types. For example:

Data Types: Python has various data types, including integers, floats, strings, lists, and dictionaries. Python infers the data type based on the assigned value.
Comments: Use the # symbol for single-line comments and ”’ or “”” for multi-line comments.
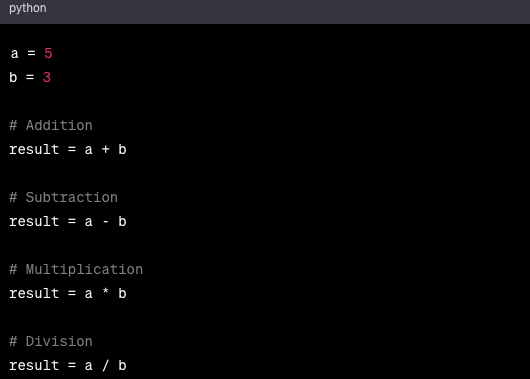
4. Basic Operations:
5. Control Flow:
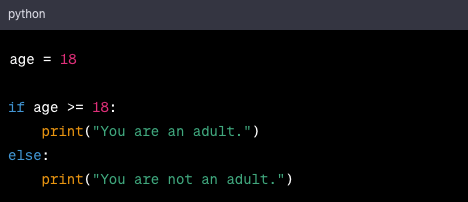
Python uses if statements for conditional execution and loops for repetitive tasks. Here are some examples:
if-else statement:
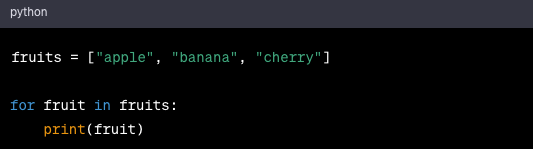
for loop:
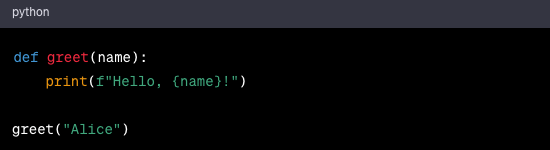
6. Functions:
7. Libraries and Modules:
Python has a rich ecosystem of libraries and modules that extend its functionality. You can install and use libraries like NumPy, pandas, and Matplotlib for data manipulation and visualization, among others.
To install libraries, you can use the ‘pip’ command. For example:

8. Learning Resources:
Official Python Documentation: The Python website has extensive documentation and tutorials: https://docs.python.org/3/
Online Courses: Websites like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer Python courses for beginners.
Books: Consider reading books like “Python Crash Course” by Eric Matthes or “Automate the Boring Stuff with Python” by Al Sweigart.
Practice: Coding exercises and challenges on websites like LeetCode and HackerRank can help you practice Python programming.
Remember that learning to program takes time and practice, so be patient with yourself as you progress. The more you code and explore Python, the more proficient you’ll become.









No Comments
Leave Comment